GUANDIAO
CNC machining is the manufacture and processing of parts and products under computer control
Numerical control processing involves the use of computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools to reshape and resize a piece of material (ie, a workpiece) by automatically removing material. Normally, the material used is plastic or metal, and when the removal is complete, the finished product or product has been produced.
This process is also called subtractive manufacturing. In order to perform CNC machining, computer applications are used to control the movement of the machine tool.
Common types of CNC machine tools
The CNC machining process includes the most common milling and turning, followed by grinding, EDM and so on.
Milling
Milling is the use of a rotating tool on the surface of the workpiece, moving along 3, 4, or 5 axes. Milling is basically cutting or trimming the workpiece, which can quickly process complex geometric shapes and precision parts from metal or thermoplastics.
Turning is the use of a lathe to manufacture parts containing cylindrical features. The workpiece rotates on the shaft and contacts the precision turning tool to form rounded edges, radial and axial holes, grooves and grooves.
Advantages of CNC machining
Compared with traditional manual machining, CNC machining is much faster. As long as the computer code is correct and conforms to the design, the finished product has a high dimensional accuracy and small errors.
CNC manufacturing is an ideal rapid prototyping manufacturing method. It can also be used to manufacture end-use products and components, but it is usually only cost-effective in short-term production runs in low volumes.
Multi-axis CNC machining
CNC milling involves removing material using rotating tools. Either the workpiece remains stationary and the tool moves onto the workpiece, or the workpiece enters the machine tool at a predetermined angle. The more motion axes of a machine, the more complex the forming process and the faster the speed. If you want to learn UG CNC programming, you can add editor QQ: 770573829 to receive learning materials and courses.
3-axis CNC machining
Three-axis CNC milling is still one of the most popular and widely used machining processes. In 3-axis machining, the workpiece remains fixed, and the rotating tool cuts along the x, y, and z axes. This is a relatively simple form of CNC machining, which can manufacture products with simple structures. It is not suitable for processing complex geometric shapes or products with complex components.
Since it can only be cut on three axes, the processing speed may also be slower than four-axis or five-axis CNC, because the workpiece may need to be manually repositioned to obtain the desired shape.
4-axis CNC machining
In four-axis CNC milling, the fourth axis is added to the movement of the cutting tool, allowing rotation around the x-axis. There are now four axes-x-axis, y-axis, z-axis and a-axis (rotating around the x-axis). Most four-axis CNC machine tools also allow the workpiece to rotate, which is the so-called b-axis, so that the machine can act as both a milling machine and a lathe.
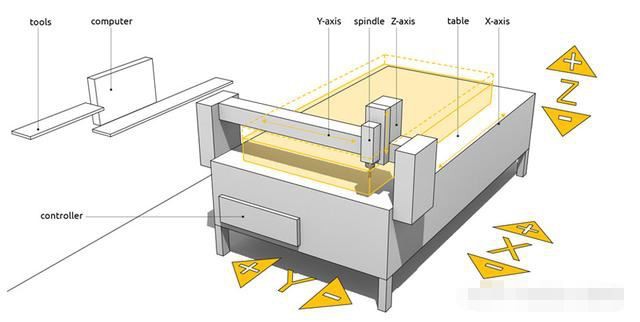
If you need to drill holes on the side of a part or on the curved surface of a cylinder, 4-axis CNC machining is the best choice. It greatly speeds up the machining process and has high machining accuracy.
5-axis CNC machining
Five-axis CNC milling has an additional rotation axis compared to four-axis CNC milling. The fifth axis rotates around the y axis, also known as the b axis. Workpieces can also be rotated on some machines, sometimes referred to as b-axis or c-axis.
Because 5-axis CNC machining has high versatility, it is used to manufacture complex precision parts. Such as artificial prostheses or bone medical parts, aerospace parts, titanium parts, oil and gas mechanical parts, military products, etc.
Copyright © 2024 Shandong Guandiao CNC Equipment Co., Ltd. . | All Rights Reserved Technical support:Xintuweb